IgA Nephropathy (IgAN) Progresses to Kidney Failure in the Majority of Patients1
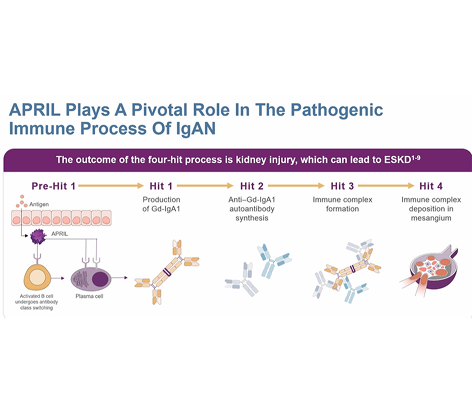
IgAN develops through the 4-hit process caused by the production of pathogenic Gd-IgA1. APRIL, a cytokine that binds to B cells, drives Gd-IgA1 production and immune complex formation.2,3

FEATURED CONTENT
Expert FAQs
Get a glimpse of our extensive video library as IgAN experts share real-world insights on pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment goals, and emerging therapies.
IgAN Simulator
Dive into the molecular world of IgAN, and simulate IgAN progression using prognostic tools and patient risk factors.

Understanding IgAN pathogenesis, progression, and management is critical for improving IgAN patient care. NephU has gathered expert-led resources and webinars to encourage ongoing disease education. Visit our Resource Center for more information.
Mechanism of Disease
Pathogenesis and the Role of APRIL
IgAN develops through the 4-hit process caused by the production of pathogenic Gd-IgA1. APRIL acts as an important initiating and sustaining driver in IgAN pathogenesis by promoting the production of pathogenic Gd-IgA1 and immune complex formation.2,3
The Role of APRIL in IgA Nephropathy
Learn about the pathogenic process that causes kidney injury and about APRIL, an important initiating and sustaining driver in IgAN.2
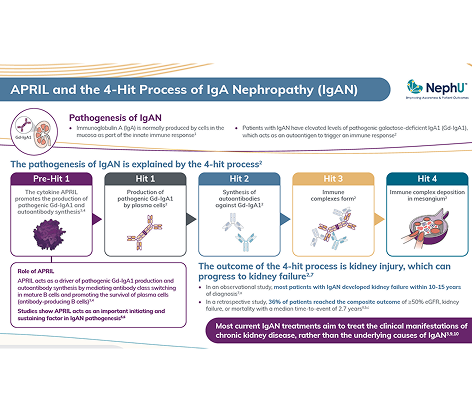
APRIL and the 4-Hit Process of IgAN
This infographic highlights the role of APRIL as an initiating and sustaining factor in the 4-hit process.2
The Immunomodulating Role of B Cells in IgA Nephropathy: Focus on APRIL
Dr Velez discusses IgAN pathogenesis and the role of APRIL, a cytokine that binds to B cells and drives IgAN pathogenesis.2

Hot Topics in Nephrology: Taking a Deeper Dive into the 4-Hit Process in IgA Nephropathy – The Role of APRIL – NephU
Dr Norouzi highlights the importance of APRIL in the initiation and progression of IgAN.2
Disease Burden and Progression
IgAN Burden and Progression to Kidney Failure
IgAN is the most common primary glomerulonephritis in the world and a leading cause of chronic kidney disease.9,10 In observational studies, most patients with IgAN develop kidney failure within 10-15 years of diagnosis.1,7,11,12

Overview of IgAN
This infographic focuses on IgAN diagnosis, prognosis, and disease management strategies.
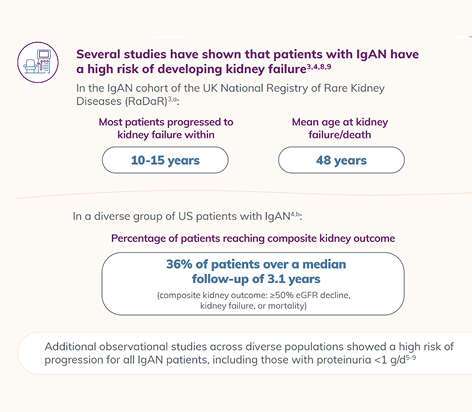
Risk of Progression to Kidney Failure in IgA Nephropathy
This infographic highlights the risk of progression to kidney failure, including in patients traditionally considered low risk.
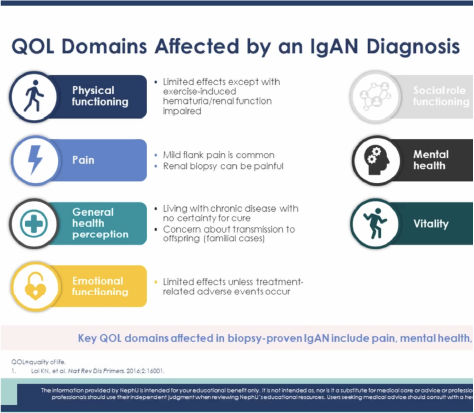
Understanding the IgA Nephropathy Patient Journey
Listen as Kelly Chen, a nephrology healthcare provider and patient living with IgAN, describes the physical, mental, and emotional toll of this chronic, progressive disease.
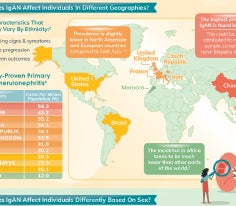
How Does IgAN Affect Individuals Based on Differences in Ethnicity, Race, and Sex?
Dr Murakami highlights how unique patient characteristics impact IgAN incidence and outcomes.
Disease Management
Risk Evaluation and IgAN Management
Despite treatment with supportive therapy, many patients with IgAN remain at risk of developing kidney failure.13
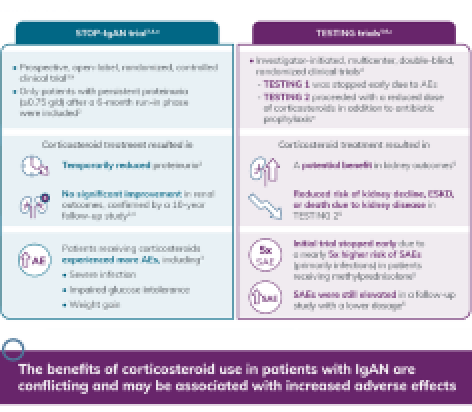
Understanding the Benefits and Risks of Corticosteroid Use in Patients With IgAN
This infographic highlights clinical trial results showing mixed efficacy and increased adverse events in patients with IgAN treated with corticosteroids.
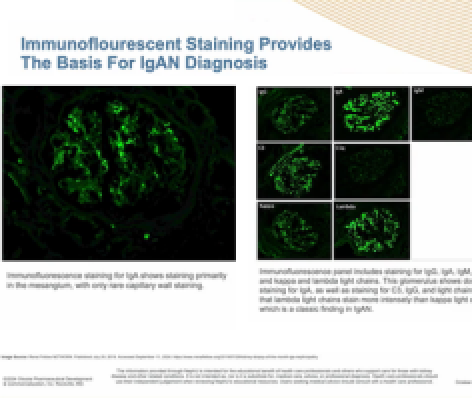
Role of the Renal Pathologist in IgA Nephropathy
Dr Hassler, a renal pathologist and patient living with IgAN, offers insights into the histopathological features that are crucial for accurate diagnosis and risk stratification in IgA nephropathy, highlighting the significance of the renal biopsy and its interpretation.
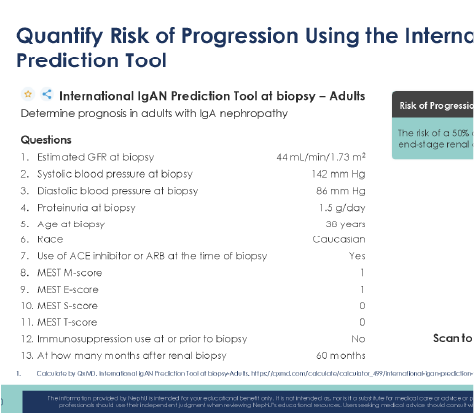
Utilization of the International IgA Nephropathy Prediction Tool
What tools can you use to assess your patient’s risk of progression based on their individual characteristics? Dr Shah explains how to harness the Prediction Tool for a more thorough evaluation.

Updates in IgA Nephropathy: Part 1 with Dr Brad Rovin
Listen as Dr Rovin, co-chair of the committee updating the KDIGO Guidelines for IgAN, discusses recent advancements in IgAN management.
HCP/Patient Dialogue
Enhancing Conversations With Your Patients
Explore real-world perspectives on managing IgA nephropathy beyond the clinic.
Mental Health Implications in IgA Nephropathy
Hear from our experts about mental health in IgAN, as well as related stressors, and how IgAN impacts patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers.
Cooking Demo: Dietary Considerations for Patients With IgA Nephropathy
Registered dietitian Lauren Levy and kidney-friendly chef Anthony Valentine bring together their expertise in nutrition and IgAN, including a review of dietary factors such as sodium and protein intake in the management of IgAN.

From Diagnosis to Management in IgA Nephropathy: How Health Literacy Shapes the Patient Journey
Learn about health literacy and how it impacts patients with CKD, including IgAN. Dr Velez will share her expertise as a nephrologist treating patients with IgAN and discuss some of the challenges seen in her own practice.

Resource Center
As a member of the NephU community, you can access a complete resource library for ongoing education. Together, we can improve IgAN care and ease the burden of this chronic, progressive disease.
APRIL, a proliferation-inducing ligand; CKD, chronic kidney disease; Gd-IgA1, galactose-deficient IgA1; HCP, healthcare professional; IgAN, IgA nephropathy; MEST-C, mesangial hypercellularity (M), endocapillary hypercellularity (E), segmental sclerosis (S), tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis (T), crescent (C).
References
1. Pitcher D, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023;18(6):727-738. 2. Mathur M, et al. J Clin Med. 2023;12(21):6927. 3. Cheung CK, et al. Front Nephrol. 2024;3:1346769. 4. Chacko B, et al. ASN Kidney News. 2024;16(1):11-12. 5. Yeo SC, et al. Clin Kidney J. 2023;16(suppl 2):ii9-ii18. 6. Moreaux J, et al. Blood. 2005;103(8):3148-3157. 7. Sim JJ, et al. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2025:gfaf084. 8. Barratt J, et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024;11:1461879. 9. Lai KN, et al. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16001. 10. Cattran DC, et al. Kidney Int Rep. 2023;8(12):2515-2528. 11. Wong K, et al. Lancet. 2024;403(10433):1279-1289. 12. Barbour SJ, et al. Kidney Int. 2013;84(5):1017-1024. 13. Lafayette R, et al. Kidney Int Rep. 2023;8(3):S258 (abstr WCN23-0383).

